Millions of observations have shown that galaxies tend to clump together in clusters. Galaxy clusters, as these structures are called, are connected through filaments, much like in a giant, universal spider web. Galaxy filaments are the largest known structures in the universe, consisting of immense networks of galaxy superclusters. In a recent study, a team found that these cosmic filaments can also play a role in how galaxies (and even individual stars) form and evolve.

Gravity is the key to forming galaxy clusters. The galaxies inside such clusters are gravitationally bound, and sometimes, they can even merge or consume each other. These interactions are not something restricted to distant corners of the universe — they’re happening in the Milky Way as well, with our galaxy set to collide with Andromeda, and we’ve also seen signs of such events in the past. As they merge and dance in the universe, galaxies change their shapes and composition, a process that is well studied in local groups of galaxies, but less explored in bigger structures.
Past studies used model simulations to understand the influence of the cosmic web in galaxy star formation. It was predicted that galaxies in clusters have less gas which is the ingredient that helps form stars. But in the present study, scientists used real observations from 245 galaxies in the filaments of the local Virgo cluster from the radio telescope in Nançay, France, and the IRAM-30m telescope in Pico Veleta, Spain.
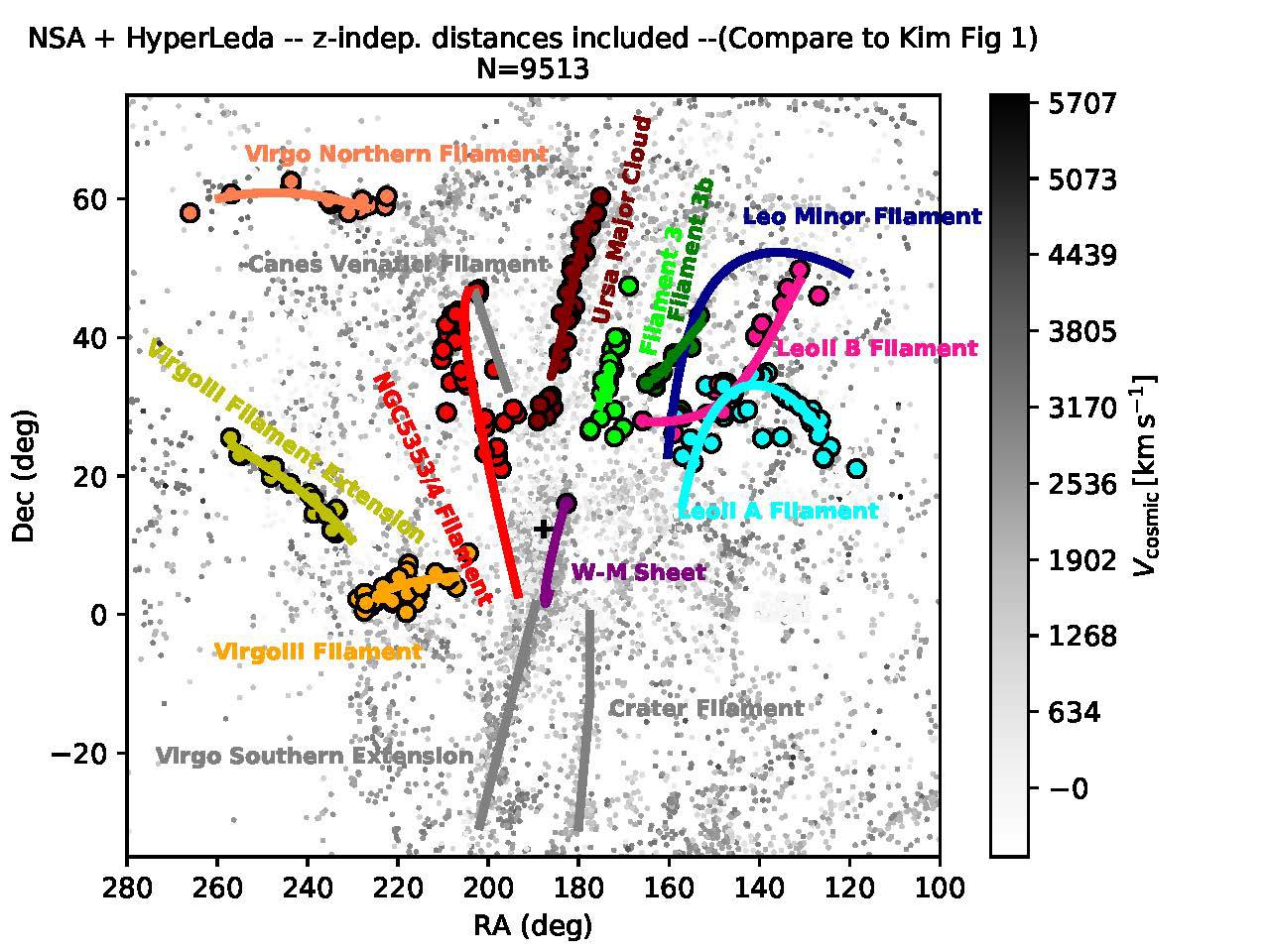
The 245 investigated galaxies contain carbon monoxide and neutral atomic hydrogen gases, key evidence that confirms whether a galaxy is forming many stars or not. The team looked at each galaxy’s distance from the center of the cluster and their corresponding filament. Their analysis showed that young galaxies are more likely to lose their gas if they form near the dense regions of the cluster. Whenever galaxies are further from the filaments or the center of the cluster, they tend to have more atomic hydrogen, which is associated with a higher star formation.
The researchers also observed that early-type galaxies tend to live in the filaments and in denser regions than younger galaxies. The most massive ones tend to live around the center of the filaments where they devour smaller neighbors and continue increasing their mass.
Based on these new insights, filaments seem to be a transitional environment, a purgatory where galaxies go before falling into a cluster. Here, galaxies slow down or stop star formation altogether. This study is the first one to show how important the cosmic web is to galactic evolution and can open up new avenues for research on theories that explain galaxy and stellar formation.
The study has been published in Astronomy & Astrophysics.









