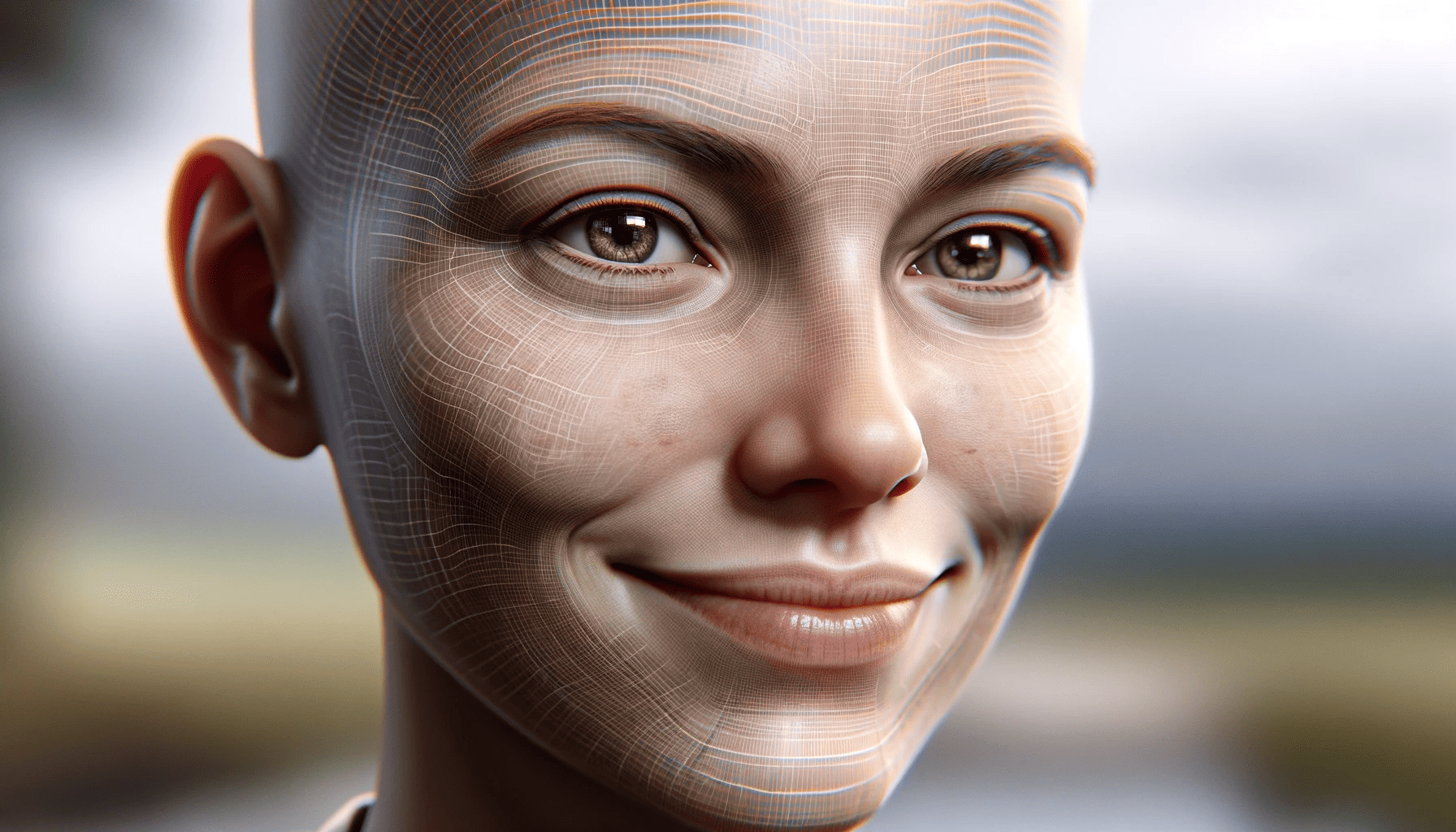
The landscape of generative AI is ever-evolving — and in the past year, it’s really taken off. Seemingly overnight, we have AIs that can generate images or text with stunning ease. This new achievement ties right into that, taking it one step further. A team of researchers led by Assoc Prof Lu Shijian from the Nanyang Technological University (NTU) in Singapore has developed a computer program that creates realistic videos, reflecting the facial expressions and head movements of the person speaking
This concept, known as audio-driven talking face generation, has gained significant traction in both academic and industrial realms due to its vast potential applications in digital human visual dubbing, virtual reality, and beyond. The core challenge lies in creating facial animations that are not just technically accurate but also convey the subtle nuances of human expressions and head movements in sync with the spoken audio.
The problem is that humans have a lot of different facial movements and emotions, and capturing the entire spectrum is extremely difficult. But the new method seems to capture everything, including accurate lip movements, vivid facial expressions, and natural head poses – all derived from the same audio input.
Diverse yet realistic facial animations
The research paper in focus introduces DIRFA (Diverse yet Realistic Facial Animations). The team trained DIRFA on more than 1 million clips from 6,000 people generated with an open-source database. The engine doesn’t only focus on lip-syncing — it attempts to derive the entire range of facial movements and reactions.
First author Dr. Wu Rongliang, a Ph.D. graduate from NTU’s SCSE, said:
“Speech exhibits a multitude of variations. Individuals pronounce the same words differently in diverse contexts, encompassing variations in duration, amplitude, tone, and more. Furthermore, beyond its linguistic content, speech conveys rich information about the speaker’s emotional state and identity factors such as gender, age, ethnicity, and even personality traits.
Then, after being trained, DIRFA takes in a static portrait of a person and the audio and produces a 3D video showing the person speaking. It’s not perfectly smooth, but it is consistent in the facial animations.
“Our program also builds on previous studies and represents an advancement in the technology, as videos created with our program are complete with accurate lip movements, vivid facial expressions and natural head poses, using only their audio recordings and static images,” says Corresponding author Associate Professor Lu Shijian.
Why this matters
Far from being only a cool party trick (and potentially being used for disinformation by malicious actors), this technology has important and positive applications.
In healthcare, it promises to enhance the capabilities of virtual assistants and chatbots, making digital interactions more engaging and empathetic. More profoundly, it could serve as a transformative tool for individuals with speech or facial disabilities, offering them a new avenue to communicate their thoughts and emotions through expressive digital avatars.
While DIRFA opens up exciting possibilities, it also raises important ethical questions, particularly in the context of misinformation and digital authenticity. Addressing these concerns, the NTU team suggests incorporating safeguards like watermarks to indicate the synthetic nature of the videos — but if there’s anything the internet has taught us, is that there are ways around such safeguards.
It’s still early days for all AI technology. The potential for important societal impact is there, but so is the risk of misuse. As always, we should ensure that the digital world we are creating is safe, authentic, and beneficial for all.
The study was published in the journal Pattern Recognition.









